The bed or linen mite is an insect so small that it is impossible to see it without a microscope. But, despite its size, it causes great harm to humans: it causes allergic reactions, rhinitis, and skin diseases. It is useful for everyone to know how to get rid of bed mites so that they no longer bother you.
Bed bugs
The bedbug or Cimex lectularius is a blood-sucking ectoparasite. The body length is 3-9 mm, the color is yellow-brown. It pierces the skin with the help of a special proboscis, and the jaws have 2 ducts, one of which is adapted for sucking blood, the second for releasing saliva into the wound. They bite at night from 3 to 8 am.
Features of the parasite:
The body has a strongly flattened shape, so it is difficult to crush the bug- They are nocturnal
- Up to 500 bites can be found on human skin in one night
- They bite only exposed parts of the body and are not able to bite through fabric.
- They live in upholstered and cabinet furniture, crevices, linen, clothes, under wallpaper and in books
- They live equally well both in dirt and in perfectly clean conditions.
- On a person’s clothes they are transferred to other houses and apartments
- Average life expectancy – 1 year
- Withstands temperatures up to 50 C
Harm to humans
Bedbug bites themselves are not dangerous for transmitting any diseases, although the possibility of transmission of tularemia, anthrax, brucellosis, and smallpox through the insect cannot be ruled out. Also, a bug bite does not cause pain.
But a significant skin rash, severe itching, allergies, unpleasant body odor, and unaesthetic appearance of the skin often bring psychological trauma to a person who, not knowing the cause of his condition, begins to look for terrible diseases within himself and withdraws into his problems. Thus, the consequences of a bedbug bite are physical and mental suffering for a person.
How to detect insects indoors?
- Brown-brown stains on bedding and underwear, which remain from insects accidentally crushed by humans.
- Accumulations of eggs, excrement and scales remaining after the bedbug molts in the grooves between parts of furniture, under furniture, in niches for linen of sofas and beds.
- Specific odor in the premises (in case of severe infection).
Symptoms of a bedbug bite
A person may not notice the symptoms of bedbug infestation for a long time or attribute the symptoms to other diseases (scabies, allergic dermatitis, etc.).
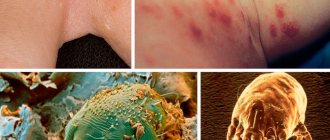
- Multiple small red spots on the body, resembling small pimples or mosquito bites. Traces of bed bug bites
- Slight swelling of the affected areas of the skin.
- Severe itching.
However, these symptoms are not always present. When biting, an adult bug secretes a special enzyme into the human skin, making its bite invisible both in sensation and appearance - there is no redness or itching. Vivid symptoms occur in people with a tendency to allergies, when premises are heavily infested, and also when young bedbugs bite them.
What do bed bug bites look like?
It is not difficult to distinguish bedbug bites from the bites of other insects. Typically this is:
multiple bites (50-100 or more). Although outwardly the bite sites are similar to a mosquito bite, in practice such a massive mosquito attack in a residential area is impossible;- a kind of bite path, i.e. red dots located one after the other at a distance of several mm to several cm. Unlike the passages of the scabies mite, the bedbug leaves such a path in one night, and the scabies mite - in several days.
Treatment of bedbug bites
There is no specific treatment for bedbug bites. Minor skin rashes resolve on their own within 3-4 days. Therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms and should be carried out in parallel with measures to combat bedbugs:
- Careful skin hygiene with detergents in the evening and morning.
- Lubricating the affected skin with hydrogen peroxide or antipruritic ointment (Fenistil) 3-4 times a day (see ointments for allergies)
- In case of a severe allergic reaction, take antihistamines for 3-5 days (Loratadine, Zyrtec, Telfast, see list of allergy pills).
How to get rid of bed bugs
The most effective is sanitary treatment of contaminated premises, which is carried out by an organization specializing in this. Very often, attempts to remove annoying insects on their own end with people simply getting rid of the infested furniture, however, this is not a guarantee that all individuals have left the living space.
Physical methods
- These include the effect of high temperature on parasites. Warming up the room for 6-8 hours at a temperature of +48 C guarantees the destruction of bedbugs and their eggs.
- At home, you can use a steam cleaner, the steam of which penetrates into hard-to-reach places, the seams of furniture upholstery, etc. This method also helps to disinfect clothes, linen, toys, etc. by heating them in dryers for about 20 minutes.
- Washing items at a temperature of at least 50 C is also effective.
Mechanical methods
This is the treatment of furniture and surfaces with a vacuum cleaner, after which the bag with parasites trapped there is destroyed. The effectiveness of the method is low due to the fact that bedbugs and their eggs may remain in places inaccessible for treatment.
Chemical methods
These include the use of insecticides, which should be used to treat furniture, cracks, baseboards, floors and other places in accordance with the instructions. The treatment should be carried out twice, the second time - two weeks after the first treatment, when young individuals can hatch from the surviving eggs.
Self-application of insecticides requires care and caution. No matter how safe insecticides are, you should not treat premises in the presence of children and pregnant women. You should strictly follow the instructions, especially the dosage of the drug, and also take personal measures to prevent poisoning.
The most effective insecticides:
GET liquid based on chlorpyrifos. Can be used in rooms where there are children. The effectiveness of the treatment provides protection against bedbugs for 6 months. The insecticide Dobrokhim Micro, which is similar in active substance, has the same properties.- Multicomponent insecticide Taran based on zetacypermethrin. The drug remains active for 2 months after treatment.
- Aerosol Raid based on cypermethrin, prallethrin and imiprothrin. Effective for 15 days.
- Boric acid, vinegar, and turpentine are also used in the fight against bedbugs, but their effectiveness is lower.
Natural Methods
These include the use of plants: tansy, fresh or dry wormwood, laid out in the most typical habitats of bedbugs - under furniture, in cracks, on the floor, etc. Treating rooms and furniture with a decoction of wild rosemary leaves also helps. These methods are safe for humans and can be used without leaving the premises.
Another natural method is to take contaminated furniture outside for several days, which is effective in sub-zero temperatures and in hot weather. Insects cannot withstand frost and direct sunlight, so they die within 24 hours. In addition, they are deprived of a power source, which accelerates their death.
They say that where cockroaches live, there are no bed bugs, since cockroaches are the latter's natural enemies. But this is not the best way to combat parasites - cockroaches, although they do not bite humans, carry various infections.
More about the parasite
One of the human companions, the linen or bed mite, lives for several hundred years and is distributed in all parts of the world. He feels comfortable with a person. It feeds on dead skin cells, dandruff, lost hair, hides in the folds of dirty bed linen, in pillows, blankets, mattresses and feels great in a dusty room that has not been cleaned for a long time.
Note! A person does not notice the presence of a bed mite if he has good immunity and does not know what an allergic reaction is.
Sensitive people have it more difficult. Their skin and respiratory organs respond to pest bites with endless runny nose, coughing, sneezing, and skin irritations in the form of a small red rash.
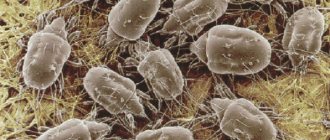
It is possible to examine a bed mite (it is a type of saprophyte) only with the help of a microscope, it is so small.
A tick (as we see it in photographs) looks like this:
- yellow-brown;
- the body is flattened, covered with chitin;
- length – from 0.2 to 0.6 mm;
- six limbs with suction cups;
- head in the shape of a triangle.
An adult tick lives for a month and a half, during which time the female lays more than three hundred eggs.
Dust mites
Dust mites, Dermatophagoides, have microscopic dimensions of 0.1-0.5 mm. There are about 150 species of dust mites. Being a synanthropic arthropod, it lives in human dwellings. The life cycle is 60-80 days. City apartments are an ideal habitat for dust mites, since they have an optimal environment for reproduction and life activity: a temperature of 20-25 C and high humidity, plus a constant source of nutrition, which is the dead epithelium lost by humans. They are found in large quantities in house dust, beds, sofas, and carpets.
Harm to humans
These small inhabitants of city apartments do not bite humans, but cause enormous harm with their vital activity. Dust mite feces contain digestive enzymes that contribute to the destruction of human skin and, when inhaled, cause severe allergic reactions, including bronchial asthma. Tick-borne bronchial asthma is characterized by spring-autumn exacerbation and night attacks.
The most common causes of dust mite fecal antigens are atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis and allergic conjunctivitis.
Symptoms of tick allergy:
- persistent rhinitis not associated with ARI, which is difficult to treat with vasoconstrictors and other drugs. It begins suddenly and also ends suddenly, in advanced cases it is present almost all year round;
- nasal congestion;
- lacrimation;
- headache;
- itching and redness of the skin, dryness and flaking;
- dry cough;
- attacks of suffocation at night.
Treatment of allergies caused by dust mites
Mite allergy is a global problem, since complete destruction of house dust mites is impossible, and every year an increasing number of people are registered with increased sensitivity to dust mite antigens, especially children (the increase in children with allergies is 6% per year).
This is the most active household allergen; the number of dust mites in 10 mcg per 1 g of dust increases the likelihood of developing bronchial asthma by 3 times.
The most effective is ASID therapy: allergen-specific immunotherapy. The method involves introducing an extract of house dust mite allergens into the body in gradually increasing concentrations. Thus, the immune system gradually gets used to the allergen, the severity of the allergic reaction decreases, and overall sensitivity to this allergen decreases. Correctly carried out treatment leads to the fact that the allergic person completely stops reacting to the allergic component of the house dust mite and gets rid of symptoms.
This method is preferable to traditional treatment with antihistamines and is used in children over 5 years of age and adults. Allergies, especially to house dust mites, are difficult to correct with anti-allergenic drugs; the body gets used to them, requiring the use of increasingly stronger drugs in higher concentrations. At the same time, a person’s immunity weakens, the body becomes sensitive to new allergens, and allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis gradually develop into asthma.
Maintaining cleanliness of the premises is of no small importance:
- carrying out daily wet cleaning
- minimizing “dust-collecting” objects: carpets, soft toys, blankets
- constant ventilation of premises
- imposing special air purifiers that supposedly clean the air, newfangled vacuum cleaners is more of an advertising ploy by the manufacturers of these products. No device can 100% get rid of dust mites. And we have no influence whatsoever on the tick infestation of public places, kindergartens, and offices.
A variety of hardening procedures, good nutrition, proper drinking regimen and a healthy lifestyle have a positive effect on the immune system and increase the body's resistance to allergens.
Fighting methods
You need to fight the linen mite using different methods:
- mechanical;
- chemical;
- natural.
Each method has its own characteristics. So, bed mites - bites, photos, symptoms, how to get rid of them.
Mechanical method
Fighting bed mites using mechanical methods means general cleaning or sanitation of the premises. At this stage, you should remove pillows stuffed with feathers and bird down, wool and cotton blankets, replace the mattress, vacuum upholstered furniture, carpets, curtains, remove dust under cabinets, beds and where seasonal clothes are stored. The vacuum cleaner bag must be thrown away immediately and replaced with a new one.
Expensive bedding can be taken to a dry cleaner, they will tell you at what temperature pests die and process the items.
Chemical method
Chemical methods of combating bed mites include special preparations, which can be purchased at household chemical stores, and disinfection of the premises. Disinfection of apartments and houses is carried out by special services; spraying strong drugs on your own is strongly not recommended.
Natural method
Natural methods are regular wet cleaning, ventilation of rooms, change of linen and bedding.
Fleas
Fleas are small insects measuring 1-4 mm in size. The body has a flattened shape, making the insect difficult to catch. They are distinguished by great jumping ability due to the presence of long hind legs and high “maneuverability” - the flea easily runs from place to place in the animal’s thick fur
The natural hosts of fleas are warm-blooded animals with fur. A person, as an organism for constant life activity, is of no interest to a flea. Fleas that can live on a person for some time and bite him are called Pulex irritans, cat fleas, Ctenocephalus telis, can also feed on human blood. They can get into a person’s home with animals, as well as on the person himself, attached to his clothing.
Harm to humans
In addition to pain at the time of the bite and constant itching after the bite, flea bites can result in serious diseases carried by these insects: plague, dermatophiliasis, pulicosis, rat typhus, rickettsiosis, tularemia, listeriosis, dipylidiosis.
Secondary infections that occur as a result of scratching wounds result in furunculosis, abscesses, ulcers and ulcers. An allergic reaction to a flea bite leads to extensive skin irritation, which can ultimately result in neurosis and insomnia.
Flea bites on a person
Most often, fleas bite on the lower extremities. When living in blankets and upholstered furniture, fleas can bite other parts of the body. When biting, the flea firmly attaches itself to the human skin and may look like a black dot.
The symptoms of a flea bite are vivid and difficult to confuse with other types of bites. By biting, the insect injects a special enzyme into the wound that thins the blood. The bite itself is accompanied by sharp pain, which turns into itching and burning. At the site of the bite, a hyperemic spot with a diameter of about 5 mm remains, in the center of which there is a bloody dot.
The spot swells, the hemorrhagic point remains visible for 3-5 days and causes significant itching. When an allergic reaction develops, urticaria occurs.
Children may also experience general symptoms, especially with multiple bites: low-grade fever, anxiety, diarrhea.
What to do if you are bitten by fleas
- Treat the bite site with an antiseptic - hydrogen peroxide, alcohol solution, potassium permanganate.
- Apply a cold compress to the bite site.
- Apply antipruritic or antiallergic ointment to the bite area.
- During the entire period of resolution of the bite on the skin, it is important not to scratch the wound, as this will lengthen the recovery period of the skin and threaten secondary infection. Soda lotions (1 teaspoon of soda per glass of water) will help relieve itching.
- If the wound does fester, you should apply a sterile cotton swab with an antibiotic-containing ointment (levomekol, gentamicin, etc.) to the abscess.
How to get rid of fleas
- Remove fleas from pets using special insecticides.
- Disinfect animal habitats - bedding, soft houses. To do this, they need to be soaked in a solution of household disinfectant, then washed in water at a temperature of about 50 C and rinsed thoroughly.
- Treat the apartment and car interior with a special insecticide, carefully following the instructions and safety rules - Tetrix, Effective Ulra, Solfak, Chlorpirimark. If necessary, treatment is repeated after 2-3 weeks.
- If you are intolerant to chemicals, you can use the herb wormwood, which should be spread around the apartment, especially on the floor and at the entrance.
- Throw away the dust bag for the vacuum cleaner, where fleas happily live and breed.
Why are bites dangerous?
Ticks are capable of transmitting many viral and other diseases, but human infection does not occur during a bite. In any case, scientists have not been able to prove otherwise. Most likely, nature made sure that bed ticks had a constant source of food. If a person becomes infected and dies, the ticks will be left without this source.
Bed tick bites are not entirely harmless. For example:
- The human body reacts in a very unique way to the bites of these parasites: severe itching, rashes on the body and other allergic reactions occur. Some people may develop angioedema, which can be fatal. About 80% of people on the planet exhibit various allergic reactions to bed tick bites.
- Some people, especially children, scratch wounds, causing them to rot.
- Iron deficiency anemia may occur, especially in children, if bites occur frequently enough.
- These parasites do not give a person normal rest at night, disturbing the person’s mental balance. No one likes having parasites suck your blood every night.
Signs of bed bug infestation, where to look and how to eliminate them
Ticks
Ticks are a real threat to rural and urban residents, from warm spring days to autumn. Every year, an increasing number of infected ticks are registered, the bite of which can cause dangerous diseases such as tick-borne encephalitis, Lyme disease and others.
Ticks attack both humans and animals in order to obtain food - blood. They react to the temperature and odors of warm-blooded animals, sensing them from a distance of 5-10 meters. While waiting for prey, they sit on plants, clinging to a person’s clothing or the fur of an animal with their front paws at the moment when the animal touches the plant. They don’t bite right away, so the victim has the opportunity to notice it and shake it off.
There are about 48 thousand species of ticks in the world.
- The most real threat comes from tick bites from the order Ixodidae, which cause borreliosis and tick-borne encephalitis (symptoms),
- Arthropods that cause various tick-borne fevers.
Ticks live not only in forests and parks; they can be found in the green area of the local area, low bushes and even grass. As a rule, vegetation does not rise above 1 m. Their sizes are small, only 2-4 mm, it is very difficult to notice a tick, and it is almost impossible to feel it on yourself at the time of the attack.
Effective methods for treating bites
The body of many people responds adequately to bed tick bites, and they heal on their own within a few days. There are people when they need to provide emergency assistance, since their body reacts very specifically. In cases where atypical reactions occur, it is necessary to:
- Thoroughly wash the bite areas with soap or soda solution, after which they are rinsed with clean running water. To prepare the solution, you need to take a glass of water and add to it a tablespoon of soda or liquid soap.
- Bite areas should be disinfected with any alcohol-containing product, such as vodka or moonshine, cologne or perfume.
- Severe itching indicates an allergic reaction. To reduce these symptoms, you can use both pharmaceutical and folk remedies.
Folk remedies
There are a number of effective and proven recipes. For example:
- Bite areas should be wiped with pure vinegar. There is no need to rinse off the product.
- You can apply a piece of ice or some product from the freezer to the bite site.
- If you apply a used bag of black or green tea to the site of the bite, this will relieve the victim of discomfort.
- Lotions are also made based on medicinal herbs. St. John's wort is considered the most effective remedy. To prepare the solution, you need to take a tablespoon of St. John's wort and pour a glass of boiling water. After the infusion has cooled, a cotton pad is soaked in the infusion and applied to the wound for half an hour. Herbs such as chamomile or calendula are suitable. The product is prepared in the same way as using St. John's wort.
- Treatment with a composition based on aloe and plantain. After mixing the ingredients, the wound is treated several times a day. The juices of these plants help reduce swelling of the bite site, reduce itching and have an antibacterial effect.
- Onion and garlic juice combined together act on the bite site in a similar way. The smell of onions and garlic, in addition to relieving discomfort, helps repel these bloodsuckers.
- You should drink at least 5 tablets of activated carbon to remove toxins from the body as quickly as possible.
As a rule, folk remedies help a person cope with negative consequences in the initial stages. If these remedies do not cope with the task, then you should use pharmaceutical remedies. Alternatively, you can use essential oils, which have the same effect as herbal infusions.
Recommended essential oils from plants such as:
- Lemon.
- Orange.
- Lavender.
- Geranium.
- Tea tree.
- Needles.
- Juniper.
- Cypress.
- Sagebrush.
- Mint.
Medications
There are both special remedies developed for the bites of various insects, and non-special ones, but which cope with this task. The thing is that each body reacts differently to bed tick bites.
As a rule, the following pharmaceutical products are used:
- Special ointments “Fenistil” and “Rescuer”. These remedies have a wide spectrum of action and help relieve the victim of negative consequences.
- Vietnamese star, which is characterized by the manifestation of an antibacterial effect.
- Afloderm helps to cope with severe itching.
- Propolis tincture is effective against any bites.
- Afloderm ointment is used with Tavegil, which helps relieve the symptoms of allergic reactions.
- The “Tsindol” talker will easily cope with the task.
- Akriderm perfectly relieves signs of inflammatory processes.
How does a tick bite occur?
It is almost impossible to detect a tick bite immediately. Tick bites are lubricated with a special anesthetic substance, so it is practically not noticeable. Particularly sensitive people may feel discomfort in the form of a nagging pain, a feeling as if a speck or butcher's broom had gotten under their clothes.
The tick tries to choose areas with delicate and thin skin, which is easier to bite through:
- neck;
- behind the ear area;
- armpits;
- code under the chest;
- groin and genitals;
- buttocks.
At the moment of the bite, the tick bites through the skin and places a hypostome, a special outgrowth of the pharynx with teeth that hold the tick, into the wound. In the process of sucking blood, the tick increases significantly in size.
If a tick is infected with tick-borne encephalitis, it retains the causative virus throughout its life. The virus enters the human blood through the saliva of the biting arthropod, so a person becomes infected in the first minutes after a tick bite; early removal of the parasite does not exclude infection with a dangerous infection. The same applies to tick-borne fevers.
If a tick is infected with borreliosis, the pathogenic bacteria enter the human blood only when the tick begins to suck blood, because live in the gastrointestinal tract of arthropods, and this is a few hours after the bite. In this case, early tick removal can prevent disease.
How to properly remove a tick - first aid for a tick bite
If it is possible to get to a medical facility as soon as possible, this should be done; doctors will quickly and without consequences remove the tick. If this is not possible, you should remove the tick yourself as quickly as possible:
Put rubber gloves on your hands and a plastic bag. Remove the tick:
- using special devices (Tick Twister, Ticked-Off, The Tickkey, Trix Tick Lasso, Anti-tick). They are always accompanied by detailed instructions for use.
- using thread. A strong thread is draped over the tick's head at the very base, i.e. near the skin in the form of a loop. The ends of the thread are carefully tightened, after which, holding the ends of the thread, you should rotate the tick clockwise or counterclockwise - a couple of movements, and the tick can be easily removed from the wound.
- using tweezers. Using the tip of tweezers, carefully grasp the head of the tick and twist it without pressing on the abdomen or tugging.
After removing the tick, place it in a glass jar.
- Remove tick remains with a sterile needle if they remain in the wound. It is best to use a sterile needle from a new syringe; in extreme cases, you can take a regular needle, hold it over the flame, treat it with alcohol a minute after it has cooled, and only then remove the tick.
- Treat the wound with an antiseptic.
- Send the extracted tick to the laboratory for testing.
What to do if an allergic reaction is detected
If suspicions are confirmed and one of the family members is found to be allergic to the linen mite, it is necessary to begin to fight it and prevent the population from increasing.
- Replace pillows and blankets. And do not buy products filled with cotton wool, wool and fluff.
- Do some general cleaning. Vacuum not only floors and carpets, but also walls, curtains, furniture, and books. Get rid of old unnecessary things.
- Change the covers of decorative pillows.
- Accustom yourself and your loved ones to regular wet cleaning and changing bed linen at least once a week.
- Replace a regular vacuum cleaner with a device with an aqua filter. In the bag of a regular vacuum cleaner, mites reproduce well.
Consequences of an encephalitis tick bite - symptoms of tick-borne encephalitis
The latent period is 5-25 days, but most often symptoms appear in the period 7-14 days after the tick bite. The general symptoms characteristic of this infection begin acutely and vividly, i.e. The patient can clearly indicate the start time of the clinic:
- heat;
- chills;
- Pain in the eyes;
- photophobia;
- pain in muscles, bones and joints;
- headache;
- vomit;
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- seizures (in children);
- redness of the sclera of the eyes, skin of the face, neck, upper body.
Forms of encephalitis
The target organ of the disease is the brain (see statistics on tick-borne encephalitis). There are several forms of encephalitis, which have their own clinical characteristics.
- Feverish form
Diagnosed in 40-50% of cases. Fever, the main symptom of the disease, lasts 5-6 days at a level of 38-40 C. After the temperature drops, the main symptoms disappear, but weakness and lethargy remain for several more weeks. Complications occur very rarely.
- Meningeal form
This is 50-60% of cases. It occurs with severe general intoxication (hyperthermia over 38 C, fever, chills, sweating, high-intensity headache), as well as symptoms of inflammation of the meninges: nausea and vomiting, decreased elasticity of the occipital and neck muscles (difficulty when trying to bring the chin to the neck), facial asymmetry, dilated pupils. Recovery is long, remission occurs in a state of weakness and weakness. Chronitization of the process is possible.
- Focal form
The heaviest downstream. Characteristics: high temperature, impaired consciousness with delusions and hallucinations, severe intoxication, convulsions, disorientation in space, impaired breathing and heart function. Most often it becomes chronic.
- Chronic form
Develops over several months and even years after the disease. Frequency - 1-3% of cases of the total number of cases. The patient experiences constant twitching of the muscles of the neck, shoulder girdle and face, tendon reflexes and muscle tone in the limbs decrease, the psyche is disturbed, and dementia develops.
Borreliosis
This disease occurs with damage to the nervous system, joints, heart, skin, and very often becomes chronic. 10-14 days after the bite, the early stage of the disease begins:
| General symptoms | Specific symptoms |
|
|
Stage of spread of infection (2-3 weeks - 2-3 months after the bite)
| Nervous system | Lumbar pain, facial pain along the nerves due to their inflammation. Decreased memory, impaired thinking processes |
| Heart | Pericarditis, myocarditis, arrhythmia |
| Leather | Transient red rash. Nodular and tumor-like elements |
| Eyes | Iritis, conjunctivitis |
| Respiratory system | Tracheitis, bronchitis |
| Joints | Arthritis and polyarthritis |
Crimean hemorrhagic fever
A severe viral disease transmitted through the bites of ticks of the genus Hyaloma. The disease is widespread in the Astrakhan, Rostov and Volgograd regions, Krasnodar and Stavropol territories, Volgograd regions, Dagestan, Kalmykia, Central Asia, China, southern Ukraine, and Crimea.
Symptoms of the disease
- Occurs within 2-14 days after the bite.
- The initial period lasts 3-4 days: severe hyperemia, intense headache, body aches, especially in the lower back, severe weakness, vomiting, lack of appetite, dizziness, impaired consciousness.
- During the peak period, there is an abrupt decrease in t - first it drops for 1-1.5 days, then it rises and lasts up to 7 days, after which it falls again. There is a petechial rash on the chest and sides of the abdomen, bleeding gums, bleeding from the ears and eyes, internal organs, and nose. The condition worsens sharply, blood pressure drops, tachycardia, lethargy, and confusion occur. The mortality rate reaches 25%.
- During the recovery period, which lasts from several months to 1-2 years, a person feels weakness and fatigue, heart pain, dizziness and headaches, and a decrease in blood pressure.
What not to do if you are bitten by a tick
- Panic. Absurd actions in such a situation are definitely not necessary. Remember - not every tick is contagious, but it’s too early to relax.
- Removing a tick from the skin with bare hands means there is a risk of the virus entering the body through micro-cuts in the skin.
- Touch eyes and mucous membranes with hands that touched the tick.
- Use oil and other liquids to deprive the tick of oxygen - in this case, the aggressiveness of the tick increases.
- Squeezing or sharply pulling out the tick will allow saliva and gastric contents to enter the wound. A sharp pull out of the tick threatens to rupture it - part of the arthropod will remain in the body.
A PEST THAT IS NOT SEEN
A dust mite (in other words – bed mite, linen mite, sofa mite, “farina”, pyroglyphide) is a microscopic arachnid insect. The average size is 0.2-0.3 mm. A specimen can only be seen well through a microscope.
An adult tick has 4 pairs of legs, a flattened body and no wings. The sensory apparatus allows you to navigate well in space even without eyes. The common name “dust mite” refers to about 150 species. Parasites live in colonies; in 1 g of dust their number varies from 10 to 30 thousand. The lifespan of an individual is up to four months. During this time, the female can lay about 350 eggs. In the apartment, dust mites live along the entire perimeter, concentrating on upholstered furniture, bedding, clothes, soft toys, bookshelves, and in dusty corners. When highly contaminated, they can be found in hair and skin. Remains of the epidermis, dandruff and hairs (their scales) serve as a source of food for them.
A person regularly supplies parasites with food, daily losing 1-2 g of the dead stratum corneum of the skin (that is why they are called synanthropic, coexisting with people). They are unpretentious to living conditions, but love high humidity and warmth. The comfort temperature range is 20-30 degrees. In an unheated room, the tick will overwinter and give birth to offspring as soon as it warms up. The parasite can be easily brought into the house. Most often it is carried with clothes in the spring and summer. The neighborhood can go unnoticed for a long time, because the tick does not bite and does not manifest itself until a certain time.
Disease Prevention
It is prescribed after examining the extracted tick if it turns out to be infectious.
- Borreliosis is a course of antibiotic therapy, depending on the drug, carried out for 5-20 days after the bite.
- Tick-borne encephalitis is the administration of immunoglobulin obtained from the blood of a person who has recovered from the disease. Very often causes serious allergic reactions. In Europe, immunoglobulin is not used; antiviral treatment is prescribed (yodantipyrine for adults, anaferon for children).
Preventing tick bites
- Wear thick clothes in light colors when visiting forests and parks. Clothing should fit tightly to the wrists and ankles. Tuck your pants into your boots.
- Wear a thick hat.
- Use special repellents that are applied to clothing or skin: Defi-taiga, Off, Ftalar, etc.
- Avoid walking past tall grass and bushes.
- After visiting the forest, carefully examine each other, as well as the animals that were with you. If the forest walk is long, check each other out after an hour, using light clearings with a minimum of vegetation. Pay special attention to the tick's favorite parts of the body.
- Do not bring freshly cut grass or branches into the house - there may be ticks there.
- People professionally associated with frequent visits to forests are vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis.
- When going to the forest, take with you everything you need that may be useful when biting a tick. Special kits have been developed: Anti-mite module.
Author:
Sabuk Tatyana Leonidovna hygienist, epidemiologist
How to get rid of bed mites at home
The linen mite is a microscopic parasite that will always be next to a person in a house where they do not like cleaning. It is difficult to get rid of the linen mite permanently, but it is possible to defeat large colonies. There are special chemical preparations that help get rid of linen mites at home, as well as folk remedies.
The use of chemicals, regular cleaning and sanitation of premises allows you to remove the maximum number of bed mites at home.
Folk remedies for getting rid of insects
Medicinal herbs and plants can help get rid of ticks. Place wormwood, rosemary and tansy in places that are difficult to reach for a vacuum cleaner and wet cleaning: their strong aromas repel pests. Regularly replace branches that have lost their aroma and shake off room dust.
For those who do not like to use chemicals, but want to remove linen mites themselves, the following recipe will help:
- take ¼ cup of liquid soap and a liter of water at room temperature, combine and stir thoroughly;
- Pour ½ cup of ammonia into the resulting solution with continuous stirring;
- Add the prepared solution to the drum of the washing machine with bed linen and wash the floors in the apartment with it.