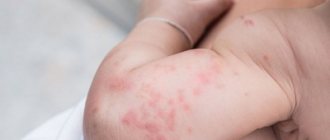
Phosphate washing powders and their harmful effects on human health and the environment.
The impact of synthetic detergents (SDC) on the environment and human health was studied back in the 60s of the last century.
- Scientific research on washing powder in the USSR
- Presence of sodium tripolyphosphate in washing powders
- Harm (surfactants) contained in washing powder
- Impact of surfactants on the environment
- Production of washing powder in Europe
- How to reduce the toxicity of washing powders
- Rules for using phosphate-based washing powders
Scientific research on washing powder in the USSR
Scientists in the USSR conducted scientific research in this area, and their results were almost identical to the results of research by foreign scientists.
The alarming facts that were revealed as a result of research were hidden not only from the consumer, but also from professionals: doctors, chemists, ecologists.
The main active ingredients of all washing powders are the so-called surfactants, which are extremely active chemical compounds.
During experiments on animals, scientists found that (surfactants) definitely change redox reactions, and (surfactants) also affect the activity of a number of very important enzymes, including disruption of protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Anions (surfactants) in pastes are especially aggressive in their actions.
They can cause serious disorders in the immune system, contribute to the development of allergies, damage to the brain, liver, kidneys, and lungs.
This is the main reason why Western European countries have imposed serious restrictions on the use of a-surfactants (anionic surfactants) in laundry detergents. At best, their content should not exceed 2-7%.
Kinds
Detergents and other compositions have a complex set of components. The chemical composition of washing powder depends entirely on the purpose and specificity of use.
Powders are:
- universal;
- for hand washing and in SMA;
- for heavy dirt;
- for delicate washing;
- for washing and disinfection;
- for removing stains;
- for colorful things;
- children's washing powders;
- powder for white;
- for washing with cold or hard water, etc.
Sources
- Anatoly, Nikolaevich Kuznetsov Criminal procedural acts 2nd ed. Textbook for secondary vocational education / Anatoly Nikolaevich Kuznetsov. - M.: Yurait, 2022. - 838 p.
- Practical accounting. Official materials and comments (720 hours) No. 6/2013 / Absent. - Moscow: Mir, 2013. - 521 p.
- Popova, E.I. The use by the investigator of the rules on the special procedure for judicial proceedings (Chapter 40 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation) / E.I. Popova. - M.: AUTHOR, 2016. - 119 p.
- A set of reviews from departments... to legitimize changes to the Code of Laws / Absent. - Moscow: Lights, 2002. - 139 p.
- Handbook of occupational safety specialist No. 5 2014 / Not available. - M.: MCFR, 2014. - 789 p.
Presence of sodium tripolyphosphate in washing powders
In addition to surfactants, washing powders contain a large amount of phosphates, or rather their derivatives - sodium tripolyphosphate (STP).
Its content in washing powder can vary from 15% to 40%. When washing, this mixture reduces water hardness and enhances the effect of washing powder.
This property is good in principle, but this small plus of a household chemical product turns into a catastrophic minus for a specific consumer, the population of the region and the country as a whole. This scale is a disaster. This was recognized in the West; they found a product with similar cleaning properties but without side effects.
What is this substance?
Phosphates are natural compounds that combine mineral phosphorus, hydrogen and oxygen. This is a class of salts produced by the chemical reaction of phosphoric acid with other elements.
Phosphates are used in the detergent composition industry and are universal. They are a key ingredient in detergents and come in liquid or powder form. Phosphates are detergent builders.
An important functional property of this substance is to increase the cleaning power of the chemical composition.
PH helps in removing grease stains. They also soften hard water. Phosphates remove mineral deposits by binding metal ions. Thanks to this, the water becomes softer and the powder removes contaminants better.
Phosphates have anti-reposition properties and help break large dirt particles into small ones, so household chemicals containing this component can remove almost any stain. This property also prevents dirt from settling on items during the wash cycle.
Harm (surfactants) contained in washing powder
Scientists have proven that 100g (surfactant) kills a horse weighing 300kg in 24 hours. Phosphate additives not only enhance the penetration of a-(surfactant) through the skin, but also increase the accumulation of this substance in fabric fibers during washing.
They promote such a strong connection of a-surfactants with the fabric that even ten times rinsing in hot water does not completely free clothing from a-surfactants.
Moreover, the more complex the structure of the fiber, the greater the number of a-surfactant molecules that can “stick” to it.
Woolen, half-woolen and cotton fabrics hold a-surfactants the strongest. On average, potentially dangerous concentrations of a-surfactants remain on tissues for up to four days.
Thus, intoxication occurs inside the human body. Having firmly attached to clothing, a-surfactant molecules, upon contact with the skin, are absorbed inside, beginning their destructive path in the human body.
Impact of surfactants on the environment
Phosphates pose a great threat to the environment; when they enter water bodies along with wastewater, they begin to act as a fertilizer.
The algae harvest in reservoirs begins to grow by leaps and bounds. When decomposing, algae release large quantities of methane, ammonia, and hydrogen sulfide, destroying all life in the water.
Overgrowing of reservoirs and water pollution leads to the cessation of water circulation in reservoirs. This leads to gross disruption of the ecosystem of water bodies, deterioration of oxygen exchange in the hydrosphere, and also leads to difficulty in providing the population with clean drinking water.
Considering the high threat to humans from phosphates, the international community has established very stringent requirements regarding the presence of phosphates in wastewater, drinking water and food. So in Western countries, the phosphate content in wastewater should be no more than 1 mg/liter.
WHAT ARE PHOSPHATES HARMFUL?
It was found that phosphates disrupt the acid-base balance , which is responsible for protection. Long-term use of phosphates results in dermatological diseases. Indeed, the percentage of allergy sufferers and allergic diseases in Russia increases every year.
Phosphates also affect the functioning of the body as a whole . Penetrating through the skin into the blood, they change the hemoglobin content, blood serum density, and protein content. As a result, the functions of the kidneys, liver, and skeletal muscles are impaired, which in turn leads to severe poisoning, metabolic disorders and exacerbation of chronic diseases.
The harm of phosphates to the environment is just as great. After washing, phosphates, along with dirty water, end up in rivers and lakes. Because of this, rapid growth of algae begins - and reservoirs turn into swamps. Fish and other inhabitants die, and the damage to nature is enormous.
Production of washing powder in Europe
In civilized countries, it has been 15 years since they introduced strict control over the content of phosphates, or abandoned them altogether. Powders that contain phosphates, chlorine or other harmful additives that cause harm to the human body can be compared to a mini Chernobyl.
World science has concluded that the safest washing powders should not contain the following chemical components: phosphates, chlorine, sulfates, silicates, ammonia, boron. The amount of anionic surfactants should be limited - no more than 2%, nonionic surfactants no more than 3%, salts of toxic acids - no more than 1%, cationic surfactants - no more than 2%, synthetic flavors - no more than 0.01% or ideally odorless .
Today in Germany, Italy, Austria, Norway and the Netherlands there is a law prohibiting the use of phosphates in washing powders.
In these countries, even car shampoo is produced without phosphates. In Belgium, more than 80% do not contain phosphates, in Finland and Sweden - 40%, in the UK and Spain 25%, in Denmark - 54%, France - 30%, Greece and Portugal - 15%. In Japan, phosphates have not been used in washing powders since 1966.
Laws banning phosphates in washing powders and other detergents are in effect in Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Thailand, and South Africa. In the US, such laws cover a third of all states.
Children's
A child, especially a newborn, is very sensitive to the environment. The baby quickly develops allergies.
When taking care of the health of your baby, choose only time-tested or folk remedies without phosphates and other harmful compounds.
Rating of the best phosphate-free children's detergent compositions:
- Denis for children is praised by many mothers, but there are also many negative reviews. It has a good composition, does not cause allergic reactions and does not contain harmful substances. However, it is difficult to wash out of the dispenser. May be served in lumps. Denis is not good at removing old stains.
- Galinka is produced by the world famous company Procter & Gamble. They can wash both children's and adult clothes. It has a neutral odor, does not contain harmful substances, and prevents the formation of scale. Galinka contains 5–15% surfactants, and less than 5% nonionic surfactants, the rest of the composition is biological. It rinses well, children do not develop allergies, and it does its job despite its natural composition.
- Our mother is a good hypoallergenic product. Does not contain harmful synthetic additives, dyes or flavors. Our mother is suitable for hand and machine washing, you can soak your laundry in it. Not suitable for stubborn stains, rinses well.
- Amway baby is a concentrated product and lasts a long time. The products from this company are expensive, but they have been tested by pediatricians, allergists and dermatologists. Amway baby has a mild cleansing formula that is ideal for baby's skin and does not irritate. The product contains no phosphates or other harmful substances. It contains only safe components that are not harmful to a child, pregnant woman or adult.
- Stork has a toxicity index of 30%. Many people claim that this remedy is good. But some sellers have added it to the blacklist. The toxicity index of Stork exceeds the permissible values. He developed an unpleasant odor. Tests were carried out in the Russian Federation and protocols were drawn up, according to which the detergent cannot be used.
The choice should be approached responsibly. Read labels carefully and look for the ECO icon on the packaging. Give preference to a safe composition, so as not to later look for the cause of cancer, poisoning and other health problems. Study baby powders especially carefully, the baby’s health depends on it.
Do not use powders with phosphates, even if they remove old stains better. Remove stains by hand, using oxygen bleach and a homemade solution, and then wash with safe detergent.
How to reduce the toxicity of washing powders
Today there are three main directions for reducing the toxicity of washing powders. The first of them is the replacement of phosphates that soften water with zeolites. Well-known manufacturers Henkel (Germany) and P&G (USA) have developed a formulation based on zeolites.
Today, phosphate-free washing powders based on zeolites are used in more than 50 countries around the world. The second direction to reduce toxicity in washing powders is the introduction of legislative restrictions and the construction of new factories (China, Thailand, India).
The third direction is the complete replacement of washing powders containing phosphates with fundamentally new third-generation powders with a new formulation, which would significantly exceed the hygienic and environmental qualities of zeolite-based powders.
As it turns out, washing powders based on zeolites, unfortunately, are also not a panacea; they also have their drawbacks:
- Low coefficient of washing out of powder residues from fabric
- High content of silicates, which leads to degreasing of the skin of the hands
- The content is more than 7% a-surfactant instead of the hygienic norm - 2%
- Cleaning ability is below the standard required
- Damage to the fabric structure and decrease in its color
As a transitional option while searching for new safe washing powders, zeolites are still suitable for scientists and consumers. But this is only for a while.