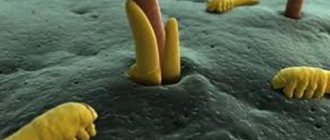
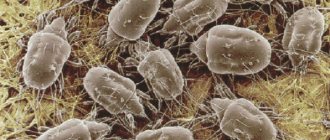
Spider mites are a common pest. Unfortunately, almost every owner of indoor plants encounters it, since it is “omnivorous” and is able to reproduce on any flowers except aquatic ones.
The tick feeds on plant sap. As a result, your favorite flowers quickly weaken and die. The pest is very dangerous. It is difficult to detect, since the size of adult individuals does not exceed 1 mm. The color of the body often blends in with the foliage and serves as an excellent camouflage. They settle on the bottom of sheets, making them even more difficult to notice.
The rapid reproduction of ticks also brings many problems. They group into colonies and inhabit an increasingly larger area of the plant. And even if the conditions for this are unfavorable, the females enter a resting stage and live up to 5 years, having the opportunity to begin the breeding cycle again at any time.
Interesting: females also “hibernate” in winter, hiding (in addition to leaves) in the soil, and even cracks in the windowsill, walls or floor.
This all complicates the process of getting rid of the pest. To save a plant, you need to understand the signs of its appearance and the features of dealing with it.
Signs of spider mites appearing on plants
You can understand that a spider mite has appeared on a plant by visual inspection. If it has already begun to actively destroy flowers, then it can be seen with the naked eye. The tick itself is a small insect no more than 1.2 mm long.
The great danger is that the life cycle of the pest is quite long - up to 40 days. Moreover, it develops into an adult within a week. More often, spider mites are smaller in size, so they are not so easy to see. The presence of an insect can be determined by signs of its vital activity.
Eggs
If the clutch is small, it is very difficult to notice it, since the size of 1 egg is less than 1 mm in diameter. It is distinguished by a white or translucent color, the shell is dense. As a rule, females lay 1-3 eggs and cover them with a layer of cobwebs to create a favorable environment for the development of insects. After 3 days the first larvae appear.
To detect such clutches, you need to carefully examine the lower parts of the leaves of the plant, the ground and the walls of the flower pot. If you can see small lumps of cobwebs, then most likely this is a clutch of spider mites.
The most dangerous thing is that even under unfavorable conditions, the eggs do not die, but are merely suspended in development. Moreover, their viability can last up to 2 years.
Thin cobweb
Spider mites on indoor plants, which are better to get rid of in the first stages of its spread, received this name because they belong to the category of arachnids. That is, it is capable of creating a web, which adult individuals can weave in large volumes. Most often, these insects cover the lower part of the leaf with cobwebs.
If the amount of such material is sufficient, then the female begins to lay many more eggs under the ready-made web, creating entire colonies of pests. But there are varieties of these insects that are not capable of creating webs. They are very rare.
If a severe infection has occurred due to the activity of spider mites, then you can see the web not only on the lower parts of the leaves, but throughout the entire plant. When dust begins to accumulate on the finest spider webs, the sign of infection becomes even more obvious.
Yellowing of leaves
Spider mites not only actively weave webs, but also feed on the sap of flowers and plants. Moreover, it can affect any zone of the above-ground part of the plant. After the mite attaches itself to a leaf or stem of a flower, a barely noticeable white spot appears in this place.
Due to the fact that the mite sucks out nutrients, the process of photosynthesis slows down, which leads to intercellular disturbances and the plant begins to slowly die.
Gradually, there are more and more small dots in places of accumulation, which leads to the fact that the part of the plant first turns yellow and then becomes very sluggish, almost completely losing its elasticity.
Falling and dry leaves
This is the last stage of plant damage. The spots on the leaves begin to join together, they dry out and fall off. Due to disturbances in the process of photosynthesis, the flower stops growing, blooming, and looks sick. As a result, the plant sheds almost all its foliage. Only the stem remains. As a rule, in this situation it is no longer possible to save the flower and all that remains is to dispose of it.
What does it look like
It is quite difficult to see it with the naked eye. Biologists classify it as arachnid, a type of arthropod. This is due to the structure of the body - it has several legs (in adults - 8, in larvae - 6), which makes it vaguely similar to a spider.
Color varies from pale, greenish-yellow, translucent. Internal organs are visible, they look just like dark spots on the back. But there are other types that are more noticeable in color, such as bright red.
Adult females acquire an orange and reddish hue closer to winter, which makes them easier to detect on the plant. They have small “claws” on their legs that help them attach to leaves.
Ticks spin a thin web in which both adults and larvae live. The life cycle of each tick is up to 50 days.
Types of mites on indoor plants and which indoor plants are susceptible to infection?
There are quite a few varieties of spider mites. Knowing their characteristics, you can quickly detect pests on indoor plants.
| Name of spider mite | Peculiarities |
| Ordinary | The most common type of tick, which has a large population. As a rule, these mites lay eggs and first infect the undersides of leaves, and then move on to young shoots and the entire plant. Mites can be seen as small dots that move around the windowsill or in the area where plants are located. The danger of this pest is that it can quickly move from one flower to another. Roses, ficuses, and impatiens suffer the most from it. |
| Red | Most of all he likes to eat balsam and orchid juice. It begins to reproduce most actively at elevated temperatures, so it can also affect those plants for which a hotter microclimate is artificially created. |
| False | The tick is very small in size, so it is almost impossible to notice with the naked eye. Also, this insect is not capable of weaving a web. Because of this, the plant may suffer from mites for a long time, and when signs of its presence become noticeable, it will be too late. |
| Atlantic | It mainly affects exotic plants, which include palm trees and citrus fruits. However, if the mite has already infested an exotic plant, it can easily move to other flowers. This insect reproduces best in conditions of high humidity. |
| Cyclamen | Most often, the mite infects chrysanthemums, cyclamen, balsam, violet, and gloxinia. It can reproduce both on leaves and in plant tubers. The colony of this mite is very similar to a layer of dust. It reproduces best in conditions of high humidity. |
| Wide | It can settle on ficus, cactus, citrus, and euonymus. It has very high fertility, so it destroys the plant in a shorter period of time. New colonies are formed every 3 days. Externally, such a pest is very easy to recognize. In addition to dust and cobwebs, red dots will be visible that may hang from the leaves. The females of this mite hide in the cracks and folds of the plant, where they lay eggs, so it is also very difficult to detect the clutch. |
| cactus | This type of tick is also called flat tick or bryobium. Most often, the pest affects exotic plants. The presence of flare can be determined by the light stripes that appear on the leaves of plants. The eggs are also easily identified by their bright orange color. Can damage any plant in the house. |
| Clover | Most often it feeds on ficus, orchids, euonymus, and ambutylone. It mainly affects bulbous plants. The mite creates tunnels in the stem and leaves, which it fills with brown dust. |
Almost all ticks are able to adapt to different conditions. Therefore, even if an insect primarily attacks bulbous plants, after their destruction it can easily move to a violet or other flower.
Description and classification
According to the biological classification, spider mites are a family of arachnid insects that includes at least 1,300 species. These are very small (no more than 1 mm) ticks with an abdomen in the form of an elongated hemisphere, four pairs of thin translucent legs equipped with tenacious claws, and a pair of thin antennae.
An insect has several life cycles:
- egg,
- translucent light green or brown larva,
- nymph,
- an adult whose body is colored orange, red-brown, yellowish or greenish.
At high daytime temperatures, the egg develops into an adult capable of laying new eggs in just a week. If the temperature is less than 15°C, this process extends for a month. In autumn, outdoors, ticks stop feeding and look for winter shelter. However, due to the high temperature indoors, this does not happen. And if ground plants get a break at least in the cold season, then domestic crops are always susceptible to attack by the parasite.
[!] It should be noted that in open ground the tick does not pose any particular danger at all. Unfavorable conditions (high air humidity, rain) and a large number of large insects preying on the parasite greatly inhibit population growth. But greenhouses, greenhouses and indoor spaces are excellent places for the aggressor to breed.
Household and garden plants are harmed by several types of spider mites:
- Common (lat. Tetranychus urticae). The most common species, most often found on ornamental crops in open and closed ground. It is a polyphagous (polyphagous insect whose diet consists of a large number of plant species).
- Red (lat. Tetranychus cinnabarinus). Damages both ornamental and agricultural plants. In regions with a warm climate it can live outdoors, in the north - only indoors.
Common and red spider mites
- Atlantic (lat. Tetranychus atlanticus). A pest of cucumbers that lives everywhere.
- Legume (lat. Tetranychus phaselus). The main habitat is the Far East. As a rule, it feeds on crops of the legume family.
- Turkestan (lat. Tetranychus turkestani). Polyphagous, feeding on both vegetables (cucumbers, tomatoes) and ornamental plants.
Despite the diversity of species, the methods of combating them are almost identical.
Where do ticks come from?
Spider mites on indoor plants, which can only be gotten rid of if you don’t miss a single clutch or by spraying with different means, can appear for a variety of reasons.
Here are just a few of them:
- The flower was not purchased from a trusted supplier , but was taken from friends who already have spider mites in their apartment. To prevent infection of all plants, a new plant should be kept in quarantine. To do this, you need to place it in another room for several weeks and observe whether signs of the presence of ticks and other parasites or diseases appear on it.
- The plants are located next to the open window . Most often, flowers that are on the first floors of houses are infected. In this case, the pest can easily descend onto the plant from a tree or upper floor. It is also not recommended to keep flowers on unglazed balconies and loggias. In addition, you should not approach plants in street clothes.
- When transplanting or planting a plant, an infected substrate was used , purchased in a store. This can also happen if you take soil for a plant from an outdoor flower bed. To avoid such contamination, it is recommended to calcinate the soil before using it.
- The plant uses a tray, pot or tub that has not been used for a long time.
- A microclimate that is too hot and humid for flowers is created . For many pests, such conditions are optimal for rapid reproduction. Therefore, at the beginning of the heating season, it is worth removing plants from window sills and installing them further from heating radiators.
To prevent ticks from penetrating indoor plants, it is necessary to inspect the flowers daily, paying special attention to the lower part of the leaves, which is usually hidden from human eyes. This is important because it only takes a few days for the tick to form from the egg.
Pest on vegetables - how to fight?
The spider mite has preferences among vegetable crops; most often it chooses cucumbers, melons, eggplants, and peppers. Phytophages feel especially good in a greenhouse. Here they are protected from bad weather and temperature fluctuations. A high reproduction rate under favorable conditions leads to rapid infection of all vegetables.
The result of the pest’s activity is:
- mechanical damage to the back of the leaves;
- slowing down the development of the ovary;
- when a spider mite appears on cucumbers, the upper tier of the plants becomes entwined with cobwebs;
- photosynthesis processes are disrupted;
- necrosis develops, the plant becomes deformed and dries out;
- Productivity declines catastrophically.
Attention. The natural enemy of the spider mite, Phytoseiulus persimilis, is used in greenhouses to kill pests. The predator feeds exclusively on this species; it is absolutely not dangerous to plants and humans.
Methods for controlling spider mites. General rules
Getting rid of spider mites that have settled on indoor plants is not so easy, but it is quite possible.
First of all, for this you need to use several general recommendations:
- If a mite is detected on one of the plants, it must be immediately isolated in a separate room where there are no other flowers. It must be kept in another room until the last tick can be eliminated. If such a plant is returned to other flowers and there is at least one viable egg on it, the entire collection may die.
- The place where the flower pot stands needs to be washed periodically with soapy water.
- For any type of treatment of the above-ground part of the plant against ticks, it is necessary to cover the soil with polyethylene. Otherwise, ticks may fall down and hide in the soil. After processing, the polyethylene must be thrown away.
- If a part of the plant is severely damaged by mites, it is better to remove the diseased leaves and stem (if possible).
- You cannot constantly treat the plant with the same anti-spider mite agent. Insects can develop immunity.
- Even if the treatment does not show any signs of mites, it is worth performing another 1-2 treatments to ensure the destruction of all eggs and individuals that could be hiding in hard-to-reach places.
- After successfully getting rid of spider mites, it is recommended to transplant the plant into a new pot and use new soil for replanting.
Washing plants with a shower is used as a preventive measure and to get rid of spider mites.
To prevent mites from appearing after purchasing pots or when using old pots, you must first wash them thoroughly using dishwashing detergent. Also, under no circumstances should you leave fallen leaves or flowers on the ground.
It is also worth considering that spider mites are not only dangerous in themselves, but also provoke the development of many diseases. For example, against the background of its life activity, gray rot may develop or fungal spores may form.
Safety precautions when treating with insecticide
I take the treated plants outside in the summer or into the bathroom if the treatment takes place in the cold season. You cannot spray Actellik in the presence of children and animals, since it is a hazard class 3 drug. Smoking while spraying is strictly prohibited.
- Root mite
In order to protect myself from the toxic effects of the drug, I wear gloves, a cotton respirator from a hardware store and a thin polyethylene raincoat. After treating the plants, I thoroughly wash the bath with soap, rinse with running water from the shower, throw away the mask, gloves and cape and take a shower.
In particularly advanced cases or for your own peace of mind, repeat the treatment after 10-12 days. And don’t count on the fact that ticks won’t appear again: you need to be very careful with these pests.
More information about spider mites
Chemicals
Spider mites on indoor plants, which are most difficult to get rid of when large colonies of insects have formed, cannot withstand chemical treatment. When using such drugs, you must carefully study the instructions.
When working with most drugs, you need to use safety glasses and avoid getting the drug on your skin and mucous membranes. Also, animals should not be allowed in the room during spraying. Otherwise, vapors of chemical or toxic agents can cause quite severe poisoning.
Aktellik
This is an effective remedy against spider mites, which is made on the basis of pirimiphos-methyl.
Influence on insects is carried out by contact method. Actellik affects the intestinal system of insects, as a result of which the process of digestion of food stops and the pest dies.
A preparation of this type is widely used in agriculture for the treatment of grain, sea buckthorn, tomatoes, cucumbers and many other crops that can suffer not only from spider mites, but also from many other pests.
To treat a plant with Actellik, you need to dilute 2 ml of the substance in 2 liters of water and spray the affected flowers with a spray bottle. Treatment is performed twice with a break of 1 week.
Fitoverm
This product is very toxic to ticks, aphids and other pests. As a rule, already at 3-5 the effect becomes noticeable and the insects begin to die. However, after the first treatment it is impossible to destroy all mite eggs. Therefore, after 7-10 days, Fitoverm is re-applied.
However, you cannot perform more than 4 sprayings, as this will have a detrimental effect on the condition of the plants themselves. You need to dilute an ampoule of the product in 1 liter of water and spray it.
Neoron
The drug is effective against all types of mites, including those that attack plants and fruit crops growing in the garden. Neoron already after the first treatment destroys the clutches of ticks, so most often repeated treatments are not required (you can carry out another spraying a week later as a preventive measure).
The active component of the product is bromopropylate. The product is not capable of having a negative effect on bees, so treatments can be carried out even while plants in the garden are flowering.
To prepare the solution, you need to dissolve 12.5 ml (1 ampoule) in a bucket of water and apply the treatment using a spray bottle or cotton wool soaked in the product. It is important to treat all leaves and stems of plants.
Flumite
Flumite belongs to the category of ovicidal agents. The drug is very effective against tick eggs and adult ticks. Due to its high toxicity, the product is recommended to be used only in very difficult situations when the mite has affected most of the plant. Mono treatment should be performed no more than once a month.
Skelta
This product also allows you to get rid of adult insects and larvae. The effect is noticeable on day 5. Skelta is often used in agriculture to cultivate large areas.
The concentration of the product should be 0.1%. That is, for 1 liter of the drug you need 1000 liters of water. Accordingly, to treat indoor plants, you need to calculate the amount of product depending on the flower collection.
Anti-mite
This drug has an effect on ticks for 2 weeks, so even if some insects do not die immediately after treatment, this will definitely happen after some time, so usually additional spraying is not required.
The product should be diluted on the basis that 10 ml of product is required per bucket of water (10 l).
Reasons for appearance
A spider mite attack is an unpredictable thing. The pest can appear in the most unexpected places: for example, on barely planted seedlings of tomatoes or cucumbers, or on your favorite lemon tree, which has been growing in the apartment for many years.
Microscopic pests and eggs spread through:
- Free-ranging animals;
- When there are gusts of wind;
- Human;
- Contaminated soil;
- Infected planting material (seeds, shoots, cuttings).
The pest overwinters in fallen leaves and soil.
Over the course of a year, from 10 to 20 generations can grow in an apartment, from 10 to 15 in a heated greenhouse, and 3-4 generations in a greenhouse without heating or on the street. Spider mites pierce leaves and stems, feed on plant sap and are absolutely unpretentious in food. It settles on indoor plants, weeds, vegetables, tops of root crops, shrubs and trees. The pest, which itself is a carrier of diseases, can introduce viral and fungal infections, mainly gray rot, into the puncture sites.
Folk remedies
Due to the fact that chemicals in most cases are also dangerous for people, many people prefer to use folk remedies. They can also be very effective, especially if the mite has just started on plants.
Garlic infusion
To prepare this simple remedy, you need to infuse 2 heads of garlic in 1 liter of water for 5 days. After this, the liquid must be filtered through cheesecloth and sprayed on the affected plants.
Onion infusion
In this case, you need to steep 2 onions in 1 liter of boiling water for 1 day. After filtering, it is better to dilute the solution with another 1 liter of water in order to reduce the concentration and means and not harm the plant itself during spraying.
Alcohol
For this product you will need ammonia, 3 ml of which must be diluted in 1 liter of water. The plant needs to be sprayed or wiped.
Rubbing alcohol and isopropyl alcohol should not be used. The plant will die from such substances.
Soap solution
To prepare the product, you need to dissolve 25 g of soap in 1 liter of warm water and add 2-3 drops of ammonia. It is best to use tar or boric soap for the product.
Vodka diluted with water
To prepare the composition for spraying, you need to dilute vodka and water in a 1:1 ratio. You cannot increase the concentration, otherwise the plant will get burned.
Dandelion root infusion
To prepare this remedy, you need to very finely chop 30 g of dandelion roots. After this, they must be infused in 1 liter of water for 2 days.
Decoction of cyclamen tubers
To prepare the product in 1 liter of water, you need to boil crushed cyclamen tubers for half an hour. After this, the broth must be covered with a lid and wait until it cools completely. All that remains is to spray or wipe the plant.
Infusion of calendula flowers
You can use dried or fresh calendula flowers. They will need 1 tbsp. The flowers must be poured with 1 liter of boiling water and left until the mixture cools completely. After this, you need to strain the liquid and treat the plants.
Laundry soap
For processing you will need 72% laundry soap. You need to create a thick foam from it and cover the entire plant with it. In this state, the flower must be left for 2-3 hours until the soap is completely dry.
Cinnamon stone
Brownstone is made from cinnamon oil. It is not sold everywhere, but if you managed to buy it, then the treatment must be performed every 3 days for 3 weeks. The product is effective only against adult insects.
Instructions for treating home flowers
Spider mites on indoor plants, which can be gotten rid of using folk remedies or chemicals, affect a wide variety of plants. Depending on the type of flower, you can get rid of the pest more effectively.
Orchid
To prevent the appearance of mites, it is recommended to wipe the axils of the leaves from stagnant water. Rot and mites can also appear on the orchid due to excessive moisture.
Spider mites on an orchid
To treat a plant, it must be completely immersed once in water with the addition of an acaricide. After this, the plant needs to be dried well with napkins.
Indoor rose
These plants are most often affected by spider mites, so it is important to inspect the plant's leaves daily. If you suspect a tick, you need to wash the flower in water at a temperature of about 50°C with the addition of melted laundry soap.
After this, the plant must be wrapped in polyethylene for a day. The next day, you only need to rinse the plant in the shower. Additionally, you can treat the flower with garlic infusion.
Ficus
As a preventive measure against spider mites, plants should be sprayed periodically. If the mite has already appeared, then the leaves on both sides need to be treated with a cloth soaked in a soap solution.
After this, the plant also needs to be kept in a plastic bag for a day and washed with warm water. Additionally, you can spray the plants with an alcohol solution. Ficus needs to be kept in a sunny place, as spider mites do not tolerate ultraviolet light.
Anthurium
If a mite is found on the plant, it is also recommended to completely wash the anthurium with soap suds. After this, it is necessary to inspect the leaves again and assess the degree of infection.
If the damage is serious, then it is necessary to remove the plant from the pot, cut off the damaged parts of the rhizome and replant the flower in a new container with the addition of fresh substrate. In difficult situations, treatment can be performed using specialized chemicals.
Violet
To ensure that this flower does not get sick and pests do not appear on it, spraying with water should be avoided, since the leaves of this plant are very sensitive to it. Therefore, it is recommended to water the violet only at the root.
If spider mites and their clutches are found on a plant, then all damaged leaves and flowers must be removed. After this, it is recommended to perform treatment with Fitoverm and repeat it after 10 days.
Dracaena
If spider mites have infested this plant, then you need to wash the dracaena leaves well in the shower using a soap solution based on tar soap. If the treatment does not produce results, it is recommended to use Fitoverm.
To get rid of spider mites, you need to inspect your indoor plants. If the first signs of a pest are detected on the foliage, it is important to carry out treatment as quickly as possible. It is useless to get rid of insects mechanically, so only chemical treatments or infusions made from natural products will help.
Preventive measures
Eliminating spider mites in a greenhouse is a very difficult task. It often exhausts the gardener and gardener, who at a certain point is ready to simply give up. In order to prevent the parasite from spoiling your nervous system, it makes sense to take all the necessary preventive measures. They will protect your greenhouse from ticks, although not 100%, but 80% for sure. And this is already a lot!
- Crop rotation rule. If this year you grew cucumbers in a greenhouse, then next year you should definitely plant tomato seedlings there. The fact is that the mite rarely settles on nightshade trees. Unlike cucumbers, the bushes of which he absolutely adores. Alternating tomato and cucumber plantings is the key to success and is effective in preventing the spread of small pests.
- Weeding is required. Cucumbers must be weeded during the growing season; under no circumstances should weeds be left in the greenhouse. The same applies to cleaning at the end of the summer season: the remains of weeds and cultivated plants from the greenhouse must be removed and burned. The earth should be dug up. Otherwise, you will leave many locations where spider mites can easily overwinter, hiding from the frost.
- Maintaining high humidity. High humidity in a greenhouse has a beneficial effect on plant development. But ticks really don’t like it. If you manage to maintain the hygrometer readings at 85-90%, rest assured: the pests will escape on their own, without waiting for the moment when you take up the chemical weapon.
- Maintaining distance. Another important point is maintaining a distance between seedlings at the time of planting. If the cucumber bushes are located too close to each other, spider mites will easily move from the destroyed plant to a healthy one - in order to destroy it too. Another effective option is to delimit cucumber bushes with other plants. For example, the same tomatoes that ticks hate so much.
When buying cucumber seedlings, do so with the understanding that the plants may be infected. Examine them carefully, looking under the leaves. Continue inspection during the growing season. This will allow you to identify the problem in a timely manner and begin solving it as soon as possible. Keep the greenhouse clean and tidy, and water the greenhouse crops on time. Strict adherence to the watering schedule and time distances between chemical treatments is the key to a large harvest of cucumbers.
Read: Temperature changes in a greenhouse: what are the dangers
Join our Facebook group